The Future of Automated Guided Vehicles in Smart Logistics
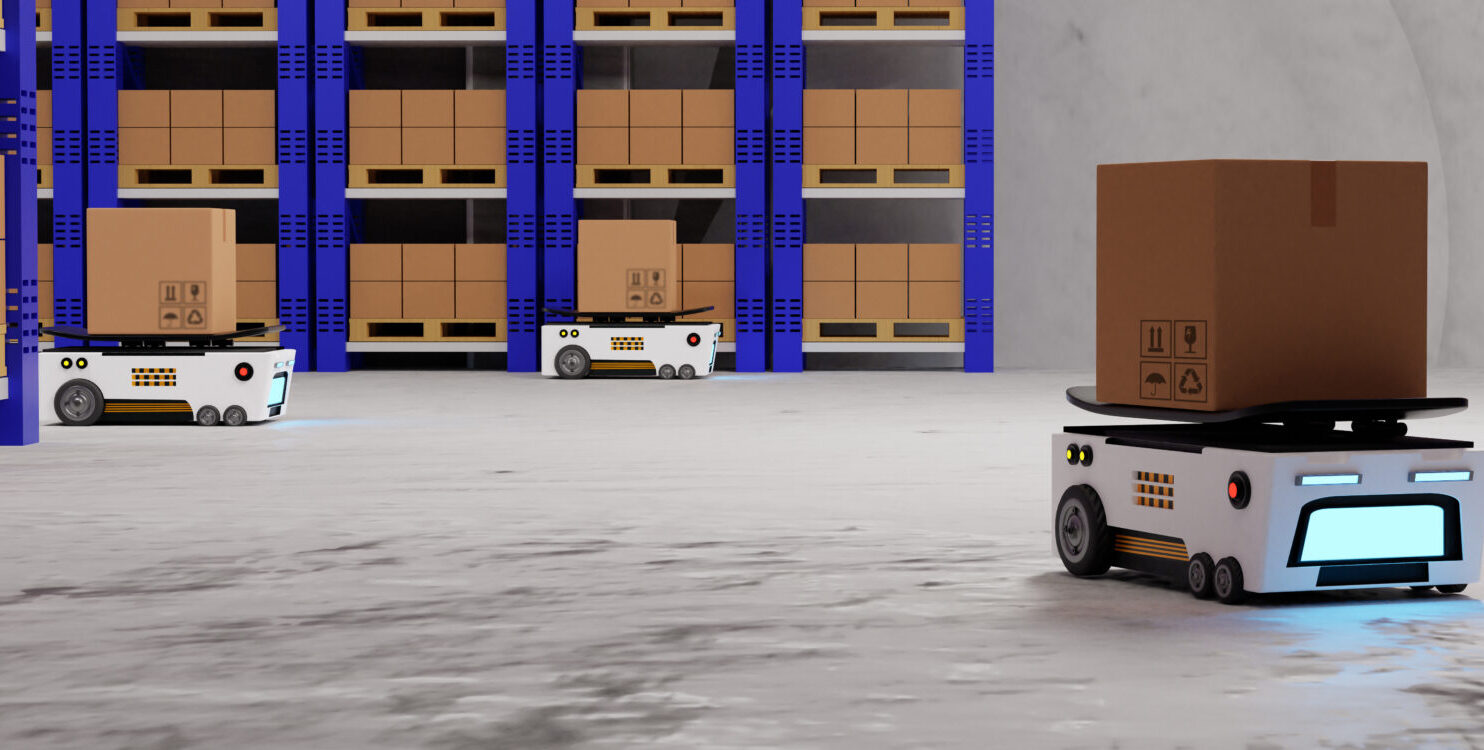

Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs) are transforming logistics operations by introducing precision, efficiency, and adaptability in material handling and inventory management. As logistics evolves with the adoption of Industry 4.0 technologies, AGVs have become a cornerstone of smart logistics systems. These intelligent machines navigate autonomously, integrate with interconnected ecosystems, and bring about a new era in warehouse and supply chain management. As per the Consegic Business Intelligence analysis Automated Guided Vehicle Market size is estimated to reach over USD 7.97 Billion by 2031 from a value of USD 3.82 Billion in 2023 and is projected to grow by USD 4.12 Billion in 2024, growing at a CAGR of 9.6% from 2024 to 2031. This article delves into the future of AGVs and their role in shaping the logistics industry.
Read also: How Autonomous Mobile Robots (AMRs) are Revolutionizing Warehouse Operations and Logistics
Advancements in Navigation and Control
One of the primary innovations driving the future of AGVs is their ability to navigate complex environments with minimal human intervention. Traditional AGVs relied on fixed tracks or magnetic tapes, limiting their flexibility. Modern AGVs use advanced LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging) and vision-based navigation systems, enabling them to dynamically map environments, detect obstacles, and adapt to changing layouts. This adaptability makes them ideal for smart warehouses with constantly evolving operations.
The integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) allows AGVs to make real-time decisions. For instance, they can prioritize tasks, reroute themselves in case of congestion, or collaborate with other AGVs to optimize workflows. These capabilities enhance operational efficiency and reduce downtime.
Interconnectivity in Smart Warehouses
AGVs are integral to the connected ecosystems of smart warehouses, enabling seamless coordination between machines, systems, and human operators. With IoT sensors embedded in AGVs, these vehicles can communicate with Warehouse Management Systems (WMS) and Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) platforms. This real-time data exchange facilitates precise inventory tracking, order fulfillment, and maintenance scheduling, ensuring smooth operations.
Cloud platforms are revolutionizing AGV fleet management. Operators can monitor vehicle performance, analyze operational data, and deploy updates remotely. This scalability and centralized control ensure consistent performance across multiple locations.
Enhanced Capabilities for Diverse Applications
The future of AGVs extends beyond warehouses, with new capabilities catering to a wide range of industries and use cases. Developments in robotics are enabling AGVs to handle heavier loads, making them suitable for industries such as automotive, construction, and steel manufacturing. These AGVs utilize robust sensors and durable materials to operate safely in demanding environments.
AGVs are being designed to work in specialized conditions, such as cold storage facilities or hazardous environments where human presence is risky. Their ability to maintain consistent performance under extreme conditions expands their utility across various sectors.
Sustainability in AGV Operations
As sustainability becomes a priority, AGV designs are evolving to align with eco-friendly logistics practices. AGVs are increasingly powered by energy-efficient lithium-ion batteries, which offer longer operational cycles and reduced charging times compared to traditional lead-acid batteries. Regenerative braking systems are also being incorporated to recapture energy and minimize wastage.
Manufacturers are using recyclable and sustainable materials in AGV construction to reduce their environmental footprint. Additionally, the modular design of modern AGVs facilitates easy upgrades and reduces the need for complete replacements.
Challenges and Future Prospects
Despite their transformative potential, AGVs face challenges such as high upfront costs, cybersecurity risks, and compatibility issues with legacy systems. However, advancements in technology and decreasing costs are making AGVs more accessible to businesses of all sizes.
Emerging technologies like 5G and edge computing promise to further enhance AGV performance, enabling faster communication and real-time processing. Additionally, the integration of collaborative robots (cobots) and AGVs will create hybrid systems that combine the strengths of both technologies.
Conclusion
The future of Automated Guided Vehicles lies in their ability to adapt, integrate, and innovate. As AGVs become smarter, more versatile, and environmentally friendly, they will continue to revolutionize smart logistics. With advancements in navigation, interconnectivity, and sustainability, AGVs are set to become indispensable in modern supply chain ecosystems, paving the way for a more efficient and intelligent logistics landscape.
Source: Automated Guided Vehicle Market