Chiplet and SoCs are shaping the future of software-defined cars
Recent advancements in the semiconductor and automotive sectors indicate a growing reliance on advanced technologies to meet the evolving needs of software-defined vehicles (SDVs). Honda Motor Co. and Renesas Electronics Corporation, an embedded semiconductor provider, have announced a partnership at CES 2025 to develop high-performance System-on-Chip (SoC) solutions for future vehicles. Meanwhile, chiplet technology is gaining traction as a crucial innovation in semiconductor design. The announcements highlight a convergence of technological trends to enhance efficiency, scalability, and functionality in automotive systems.

Katsushi Inoue, Senior Managing Executive Officer and Chief Officer, Electrification Business Development Operations at Honda, and Vivek Bhan, Senior Vice President and General Manager of High Performance Computing.
Chiplet technology in automotive applications
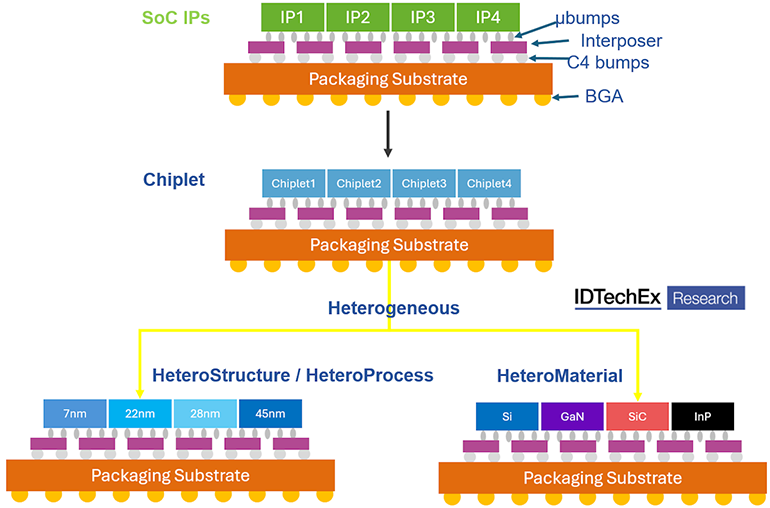
Chiplet technology overcomes limitations in traditional monolithic System-on-Chip (SoC) designs, such as reticle size, memory access, and issues related to power consumption. By modularizing chip functions into smaller, discrete components, chiplets improve manufacturing yields, reduce costs, and offer greater flexibility in system design. This modular approach facilitates easier customization and upgrades, aligning with software-defined vehicles requiring adaptable architectures.
In automotive applications, chiplets provide an efficient means of integrating multiple functionalities, such as artificial intelligence (AI), advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS), and automated driving (AD). Companies like AMD and Intel have successfully demonstrated chiplet-based designs in high-performance computing, and the automotive sector is starting to adopt similar strategies.
Honda and Renesas collaboration
Honda and Renesas recently announced plans to co-develop a high-performance SoC tailored for Honda’s 0 (Zero) Series of electric vehicles, which are set for release in the late 2020s. The SoC will be the core of a centralized electrical/electronic (E/E) architecture, consolidating functions typically managed by multiple electronic control units (ECUs) into a single, high-capacity unit.
Renesas will integrate its fifth-generation R-Car X5 series SoC and AI accelerators into the design, using TSMC’s 3-nanometer automotive process technology to minimize power consumption. Honda’s proprietary AI software will also be optimized within this system to enable functionalities such as automated driving, powertrain control, and enhanced in-vehicle systems. Utilizing chiplet technology ensures that the SoC can be customized and scaled for future updates, a crucial consideration for evolving vehicle platforms.
A shift toward centralized architectures
The shift toward centralized E/E vehicle architectures reflects a broader trend in the automotive industry. Traditional systems rely on decentralized ECUs, each responsible for specific functions. Centralized systems, in contrast, simplify hardware requirements, enhance efficiency, and improve the ability to implement advanced features like AI-driven driving systems.
This transition places significant demands on the underlying SoCs, which must deliver high computational power without surpassing strict power consumption limits. Chiplet technology, with its modular approach, is well-suited to tackle these challenges.
Implications for the automotive and semiconductor industries
The collaboration between Honda and Renesas underscores the increasing interplay between the automotive and semiconductor sectors. Chiplet technology, once primarily associated with data centers and high-performance computing, is now being adapted to satisfy the unique demands of SDVs. As vehicles become more software-driven, the ability to create modular, high-performance SoCs will be essential for their development.
The broader chiplet market is expected to grow significantly, with applications across multiple industries. For automotive manufacturers, integrating and updating advanced features without redesigning entire systems represents a competitive edge in an era of rapid technological change.